Today’s global supply chains are more complex than ever. Companies rely on multiple suppliers, cross-border logistics, and large distribution networks. This complexity often creates challenges such as lack of visibility, shipment delays, and even the risk of counterfeit products. To address these issues, businesses need better supply chain traceability. Among the available tools, RFID technology has become one of the most effective solutions to improve transparency and efficiency across supply chain operations.
Supply chain traceability refers to the ability to track raw materials, components, and finished products throughout their entire journey—from the source of origin to the end customer. This involves recording key data at every stage, including production, warehousing, and transportation.
The benefits are clear: traceability ensures product quality and safety, supports compliance with regulations, improves efficiency, and builds consumer trust. In manufacturing especially, being able to trace goods is critical for quick recalls, ethical sourcing, and maintaining brand reputation.
Although the value of traceability is clear, many organizations struggle to achieve it. Data accuracy is often a problem, since incomplete or inconsistent records can create blind spots. Global supply chains add another layer of complexity, involving multiple suppliers across different countries with varied regulations and practices.
Another barrier is the lack of standardization, which makes data sharing between partners more difficult. Some suppliers may be reluctant to share information about their processes, creating transparency issues. On top of that, the cost of technology and infrastructure upgrades can be a concern, especially for smaller businesses. Finally, compliance with evolving regulations requires constant adaptation, which adds pressure on supply chain managers.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses wireless communication between RFID tags and readers to capture data automatically. An RFID system typically consists of three parts: the tag (attached to products, pallets, or containers), the reader (which captures the tag’s data), and a database that stores and processes the information.
Compared to traditional barcodes, RFID offers clear advantages. Tags can be read without line-of-sight, multiple items can be scanned at once, and data can be updated in real time. In supply chains, both passive RFID tags (which draw power from the reader) and active RFID tags (which have their own power source) are used depending on the application.
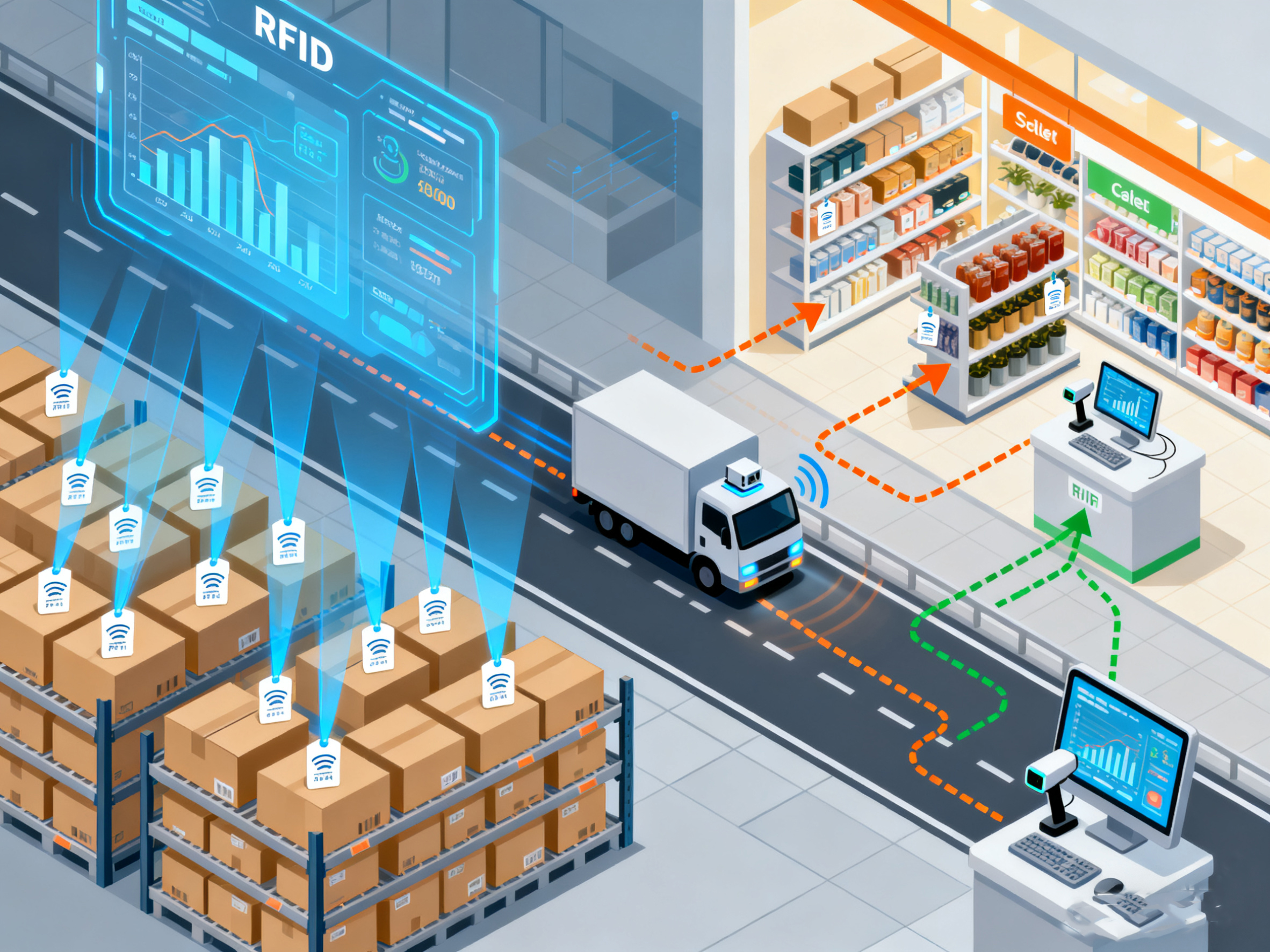
The role of RFID in supply chain traceability is significant. First, it enables automated data capture, which reduces the risk of human error and eliminates the need for manual entry. This means faster and more accurate information flow across the supply chain.
Second, RFID allows for real-time tracking of products, so companies always know where their goods are and in what condition. This visibility helps prevent losses, improves inventory management, and supports faster decision-making.
Third, RFID makes recalls and quality checks more efficient. Since every product can be linked to specific data such as origin, batch number, or expiration date, it is easier to trace issues back to the source and limit the impact on the rest of the supply chain.
Additionally, RFID helps streamline operations by automating inventory reconciliation, optimizing logistics, and reducing paperwork. This leads to faster order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction. Beyond daily operations, RFID data also supports analytics, helping businesses identify trends, detect bottlenecks, and make better forecasts.
Using RFID brings several advantages:
Efficiency: Automates processes and reduces manual work.
Accuracy: Ensures precise and reliable data capture.
Real-time visibility: Provides instant updates on inventory and shipments.
Compliance and risk management: Helps companies meet regulations and reduce vulnerabilities.
Trust and reputation: Supports transparency, which builds stronger relationships with customers and partners.
RFID is widely applied across industries. In retail, it enables fast restocking, reduces out-of-stock situations, and supports omnichannel strategies. In manufacturing, it provides full visibility of raw materials, components, and finished goods, which is essential for quality control.
In the pharmaceutical sector, RFID improves drug traceability, combats counterfeiting, and ensures cold chain monitoring. Meanwhile, in logistics and transportation, RFID enables real-time shipment tracking, reduces delivery errors, and enhances fleet efficiency. These applications highlight how versatile and impactful RFID can be across the global supply chain.
To maximize the value of RFID, businesses should start with high-value or high-risk areas before expanding to other processes. Integration with existing systems like ERP or WMS is essential to prevent data silos. Standardized data practices and collaboration among partners also ensure smooth information sharing across the supply chain.
It is equally important to invest in data security and privacy, since RFID systems involve large amounts of sensitive information. Finally, building trust with suppliers and encouraging transparency will make RFID deployment more effective.
In conclusion, RFID technology is a powerful enabler of modern supply chain traceability. It improves visibility, automates processes, ensures compliance, and supports smarter decision-making. With real-time insights and accurate data, businesses can optimize operations, protect their brand, and build stronger customer trust. As global supply chains continue to evolve, RFID will remain a key driver of efficiency and transparency.
Do you need a professional team to provide you with solutions? Contact us for a quote
Let us discuss it with you.